Drug Delivery Systems
Drug delivery systems have come a long way since the days of traditional dosage forms, which are often limited regarding targeted delivery, low efficacy, and unwanted side effects. Converting potent drugs into effective therapies requires suitable carrier systems, increasing the stability of drug molecules, enabling administration to the human body, and improving specific targeting of cells and tissues. Our team works on innovative nanoscale drug delivery systems as well as novel and creative approaches to optimize local drug delivery. Both have the potential to revolutionize the way drugs are administered and ultimately improve patient treatment.
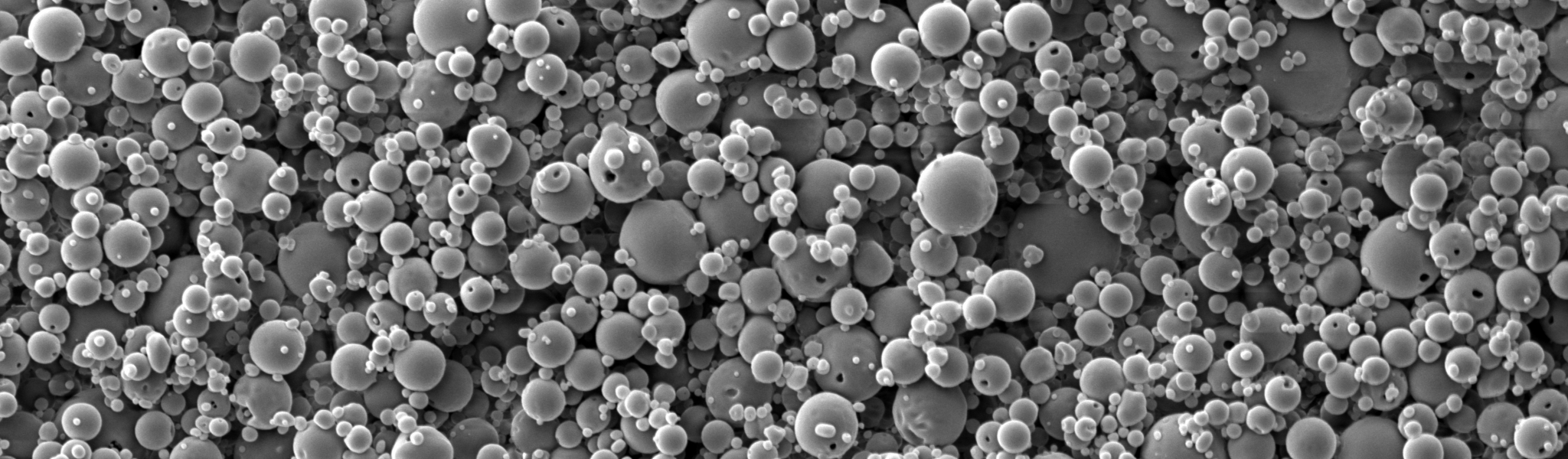
Vesicles & Particles
The targeted delivery of pharmaceutical actives to their intended site of action poses a major challenge in the establishment of new therapeutic strategies. Nanocarriers hold great potential to make drug delivery more efficient by providing a transport system, protective shield, and customizable surface to evade or specifically target different cells of the body. We are working on developing adaptive nanocarriers, based on natural or (semi-)synthetic polymers, carbohydrates, or lipids, to safely deliver cargo such as small molecules, PROTACS, RNA or proteins.
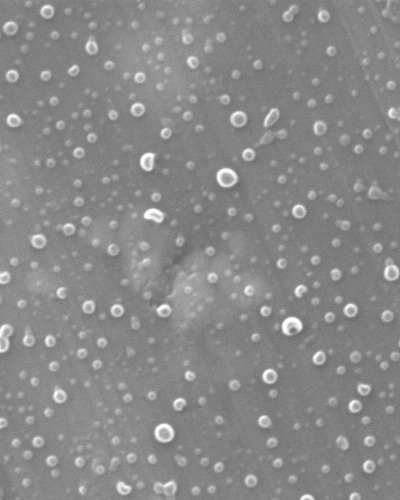
Related Publications
- Brettner FEB, Schreiner J, Vogel-Kindgen S, Windbergs M. Engineered Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Cyclodextrin Conjugates for Drug Encapsulation. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c01023
- Friedl JD, Walther M, Vestweber PK, Wächter J, Knoll P, Jörgensen AM, Bernkop-Schnürch A, Windbergs M. SEDDS-loaded mucoadhesive fiber patches for advanced oromucosal delivery of poorly soluble drugs. J Control Release. 2022; 348:692-705. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.023
- Nnamani P, Ugwu A, Ibezim E, Onoja S, Odo A, Windbergs M, Rossi C, Lehr CM, Attama A. Preparation, characterisation and in vitro antibacterial property of ciprofloxacin-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier for treatment of Bacillus subtilis infection. J Microencapsul. 2019; 36(1):32-42. doi: 10.1080/02652048.2019.1582724
Associated Team Members
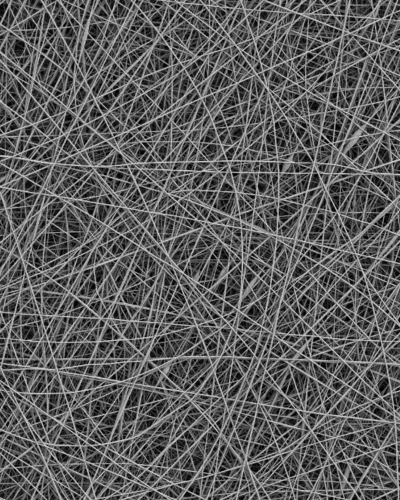
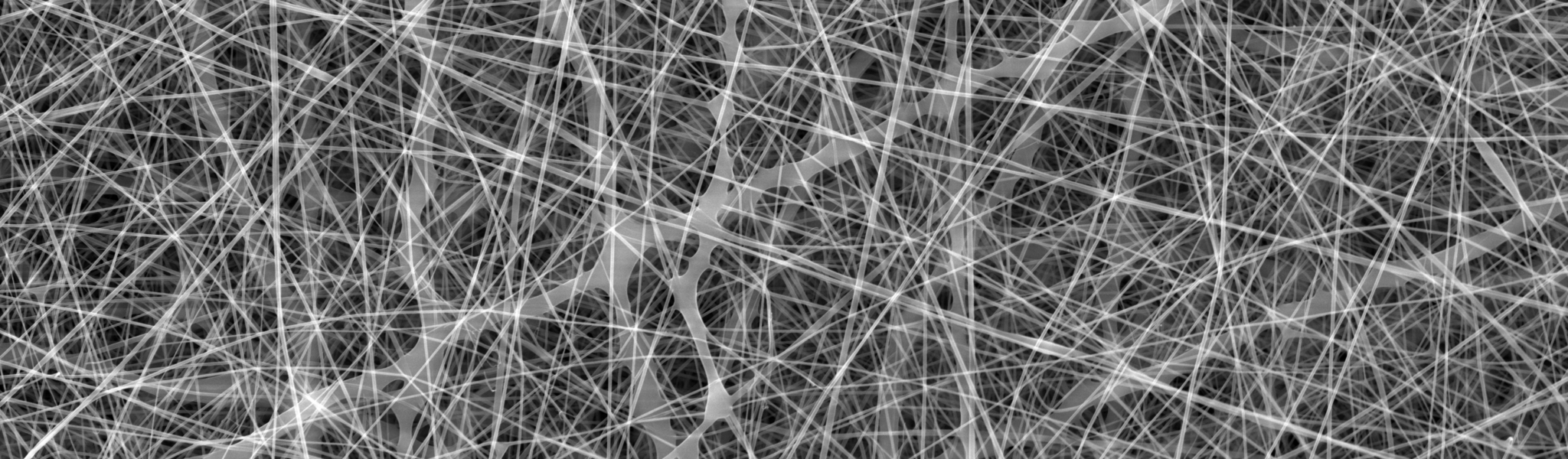
Electrospun Fibers
The task of delivering fragile drug molecules locally to skin and mucosa is a significant challenge in the field of pharmaceutical research. To combat this issue, we develop nanofibrous delivery systems for the controlled release of small molecules and biomacromolecules. By using Electrospinning, a technique utilizing high voltage to generate ultrafine polymer fibers, we design tailor-made systems that offer controllable release kinetics. Additionally, we are able to context-specifically adapt the mucoadhesive, antimicrobial, or regenerative properties of the generated fiber mats/scaffolds.
Related Publications
- Walther M, Vestweber PK, Kühn S, Rieger U, Schäfer J, Münch C, Vogel-Kindgen S, Planz V, Windbergs M. Bioactive Insulin-Loaded Electrospun Wound Dressings for Localized Drug Delivery and Stimulation of Protein Expression Associated with Wound Healing. Mol Pharm. 2023;20(1):241-254. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00610
- Kielholz T, Walther M, Jung N, Windbergs M. Electrospun fibers loaded with antimicrobial peptides for treatment of wound infections. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022; 179:246-255. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2022.09.014
- Rohde F, Walther M, Wächter J, Knetzger N, Lotz C, Windbergs M. In-situ tear fluid dissolving nanofibers enable prolonged viscosity-enhanced dual drug delivery to the eye. Int J Pharm. 2022; 616:121513. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121513
- Wang J, Windbergs M. Controlled dual drug release by coaxial electrospun fibers - Impact of the core fluid on drug encapsulation and release. Int J Pharm. 2019; 556:363-371. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.12.026
- Wang J, Planz V, Vukosavljevic B, Windbergs M. Multifunctional electrospun nanofibers for wound application - Novel insights into the control of drug release and antimicrobial activity. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018; 129:175-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.05.035
Associated Team Members
Actives
With our innovativenanocarrier platforms, we’re particularly interested in the delivery of small molecules, PROTACS, RNA, and proteins. These active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) have unique properties that make them attractive therapeutics: Small molecules can be used to target specific pathways within cells, while PROTACS enable targeted protein degradation. RNA and proteins are essential building blocks of the body, and their delivery can help treat a wide range of diseases.
Our research into nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for those APIs is essential to improve the efficiency and safety of next generation therapeutics.








